What You Need to Know About Electro-Mechanical Technician
Electro-Mechanical Technician Job Description Operate, test, maintain, or calibrate unmanned, automated, servo-mechanical, or electromechanical equipment. May operate unmanned submarines, aircraft, or other equipment at worksites, such as oil rigs, deep ocean exploration, or hazardous waste removal. May assist engineers in testing and designing robotics equipment.
Life As an Electro-Mechanical Technician
- Read blueprints, schematics, diagrams, or technical orders to determine methods and sequences of assembly.
- Repair, rework, or calibrate hydraulic or pneumatic assemblies or systems to meet operational specifications or tolerances.
- Verify part dimensions or clearances to ensure conformance to specifications, using precision measuring instruments.
- Operate metalworking machines to fabricate housings, jigs, fittings, or fixtures.
- Align, fit, or assemble component parts, using hand or power tools, fixtures, templates, or microscopes.
- Operate, test, or maintain robotic equipment used for green production applications, such as waste-to-energy conversion systems, minimization of material waste, or replacement of human operators in dangerous work environments.
Skills Needed to be an Electro-Mechanical Technician
Electro-Mechanical Technicians state the following job skills are important in their day-to-day work.
Operation Monitoring: Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Troubleshooting: Determining causes of operating errors and deciding what to do about it.
Monitoring: Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Quality Control Analysis: Conducting tests and inspections of products, services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Repairing: Repairing machines or systems using the needed tools.
Types of Electro-Mechanical Technician Jobs
- Robotics Testing Technician
- Test Technician
- Electronic Technician
- Remotely Piloted Vehicle Controller (RPV Controller)
- Rework Technician
What Kind of Electro-Mechanical Technician Job Opportunities Are There?
In 2016, there was an estimated number of 13,800 jobs in the United States for Electro-Mechanical Technician. New jobs are being produced at a rate of 3.6% which is below the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 500 new jobs for Electro-Mechanical Technician by 2026. There will be an estimated 1,200 positions for Electro-Mechanical Technician per year.
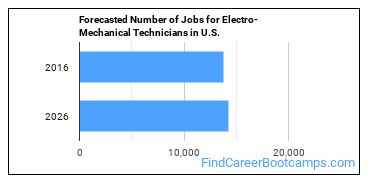
The states with the most job growth for Electro-Mechanical Technician are Idaho, Nevada, and Utah. Watch out if you plan on working in Washington, Massachusetts, or West Virginia. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
How Much Does an Electro-Mechanical Technician Make?
The typical yearly salary for Electro-Mechanical Technicians is somewhere between $37,090 and $88,860.
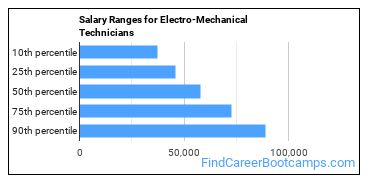
Electro-Mechanical Technicians who work in Washington, Georgia, or Colorado, make the highest salaries.
Below is a list of the median annual salaries for Electro-Mechanical Technicians in different U.S. states.
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $62,140 |
| Arizona | $58,940 |
| California | $63,830 |
| Colorado | $65,870 |
| Connecticut | $57,960 |
| Florida | $48,320 |
| Georgia | $68,690 |
| Idaho | $58,550 |
| Illinois | $65,260 |
| Indiana | $56,590 |
| Iowa | $53,840 |
| Kentucky | $49,530 |
| Louisiana | $58,450 |
| Maryland | $68,390 |
| Massachusetts | $57,710 |
| Michigan | $56,860 |
| Minnesota | $56,980 |
| Nebraska | $57,420 |
| Nevada | $51,030 |
| New Hampshire | $60,410 |
| New Jersey | $59,660 |
| New York | $67,440 |
| North Carolina | $61,510 |
| Ohio | $64,720 |
| Oklahoma | $57,640 |
| Oregon | $57,080 |
| Pennsylvania | $51,160 |
| South Carolina | $58,280 |
| Tennessee | $52,900 |
| Texas | $57,070 |
| Utah | $62,780 |
| Virginia | $56,020 |
| Washington | $81,790 |
| West Virginia | $59,830 |
| Wisconsin | $58,340 |
| Wyoming | $60,260 |
What Tools & Technology do Electro-Mechanical Technicians Use?
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Electro-Mechanical Technicians:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Outlook
- Microsoft Access
- SAP
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- Linux
- UNIX
- Computer aided design CAD software
- National Instruments LabVIEW
- Supervisory control and data acquisition SCADA software
- Dassault Systemes SolidWorks
- PTC Creo Parametric
- Computerized maintenance management system CMMS
- Autodesk Inventor
- Human machine interface HMI software
- Rockwell RSLogix
- Circuit simulation software
How do I Become an Electro-Mechanical Technician?
Learn what Electro-Mechanical Technician education requirements there are.
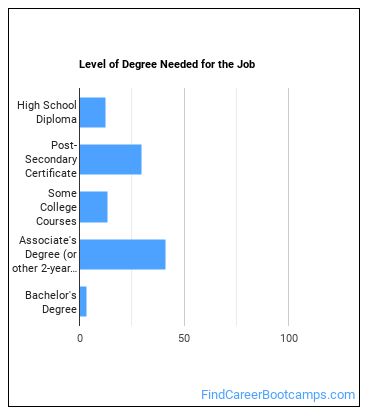
How many years of work experience do I need?
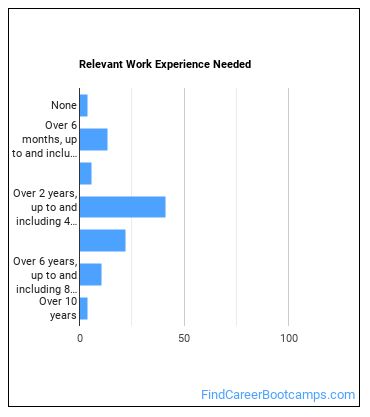
Who Employs Electro-Mechanical Technicians?
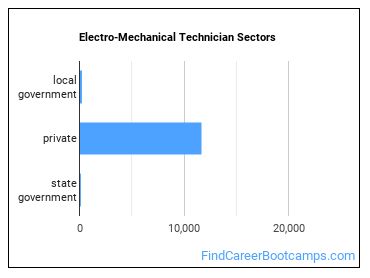
The table below shows the approximate number of Electro-Mechanical Technicians employed by various industries.
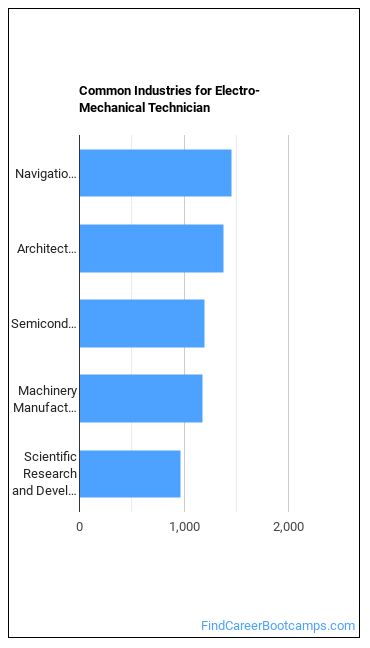
Similar Careers
Those thinking about becoming an Electro-Mechanical Technician might also be interested in the following careers:
References:
Image Credit: AAAndrey A via Public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
