What You Need to Know About Electromechanical Engineering Technologist
Example of Electromechanical Engineering Technologist Job Assist electromechanical engineers in such activities as computer-based process control, instrumentation, or machine design. May prepare layouts of machinery or equipment, plan the flow of work, conduct statistical studies, or analyze production costs.
Electromechanical Engineering Technologist Responsibilities
- Translate electromechanical drawings into design specifications, applying principles of engineering, thermal or fluid sciences, mathematics, or statistics.
- Produce electrical, electronic, or mechanical drawings or other related documents or graphics necessary for electromechanical design, using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Consult with machinists or technicians to ensure that electromechanical equipment or systems meet design specifications.
- Test and analyze thermodynamic systems for renewable energy applications, such as solar or wind, to maximize energy production.
- Determine whether selected electromechanical components comply with environmental standards and regulations.
- Fabricate or assemble mechanical, electrical, or electronic components or assemblies.
Electromechanical Engineering Technologist Required Skills
These are the skills Electromechanical Engineering Technologists say are the most useful in their careers:
Active Listening: Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Critical Thinking: Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Reading Comprehension: Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Complex Problem Solving: Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Monitoring: Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Active Learning: Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Types of Electromechanical Engineering Technologist Jobs
- Process Control Tech
- Engineering Tech
- Senior Design Engineering Specialist
- Senior Designer
- Designer
Is There Job Demand for Electromechanical Engineering Technologists?
There were about 76,800 jobs for Electromechanical Engineering Technologist in 2016 (in the United States). New jobs are being produced at a rate of 5.2% which is below the national average. The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts 4,000 new jobs for Electromechanical Engineering Technologist by 2026. The BLS estimates 7,100 yearly job openings in this field.
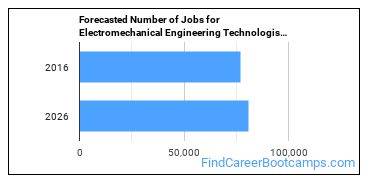
The states with the most job growth for Electromechanical Engineering Technologist are Utah, Nevada, and Connecticut. Watch out if you plan on working in Vermont, West Virginia, or South Dakota. These states have the worst job growth for this type of profession.
Salary for an Electromechanical Engineering Technologist
The salary for Electromechanical Engineering Technologists ranges between about $36,120 and $98,720 a year.
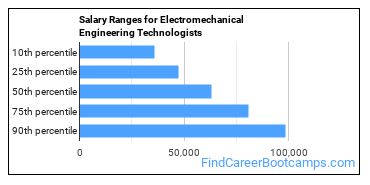
Electromechanical Engineering Technologists who work in District of Columbia, Maryland, or Maine, make the highest salaries.
How much do Electromechanical Engineering Technologists make in each U.S. state?
| State | Annual Mean Salary |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $59,380 |
| Alaska | $71,850 |
| Arizona | $59,210 |
| Arkansas | $60,310 |
| California | $71,420 |
| Colorado | $63,590 |
| Connecticut | $64,510 |
| Delaware | $51,380 |
| District of Columbia | $92,600 |
| Florida | $58,860 |
| Georgia | $59,830 |
| Hawaii | $76,070 |
| Idaho | $55,540 |
| Illinois | $63,760 |
| Indiana | $58,450 |
| Iowa | $57,620 |
| Kansas | $65,870 |
| Kentucky | $58,880 |
| Louisiana | $59,930 |
| Maine | $79,670 |
| Maryland | $84,790 |
| Massachusetts | $64,220 |
| Michigan | $64,270 |
| Minnesota | $57,440 |
| Mississippi | $60,500 |
| Missouri | $59,830 |
| Montana | $59,810 |
| Nebraska | $57,630 |
| Nevada | $71,330 |
| New Hampshire | $57,730 |
| New Jersey | $75,380 |
| New Mexico | $78,160 |
| New York | $63,780 |
| North Carolina | $63,600 |
| North Dakota | $75,030 |
| Ohio | $61,060 |
| Oklahoma | $63,790 |
| Oregon | $56,890 |
| Pennsylvania | $57,210 |
| Rhode Island | $73,240 |
| South Carolina | $70,820 |
| South Dakota | $51,110 |
| Tennessee | $57,800 |
| Texas | $66,630 |
| Utah | $56,480 |
| Vermont | $58,960 |
| Virginia | $77,280 |
| Washington | $74,810 |
| West Virginia | $70,550 |
| Wisconsin | $58,780 |
| Wyoming | $67,110 |
What Tools do Electromechanical Engineering Technologists Use?
Although they’re not necessarily needed for all jobs, the following technologies are used by many Electromechanical Engineering Technologists:
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Access
- Autodesk AutoCAD
- The MathWorks MATLAB
- Computer aided design CAD software
- National Instruments LabVIEW
- Dassault Systemes SolidWorks
- PTC Creo Parametric
- The MathWorks Simulink
- Autodesk Inventor
- Rapid prototyping software
- Rockwell RSLogix
- National Instruments Multisim
Becoming an Electromechanical Engineering Technologist
Individuals working as an Electromechanical Engineering Technologist have obtained the following education levels:
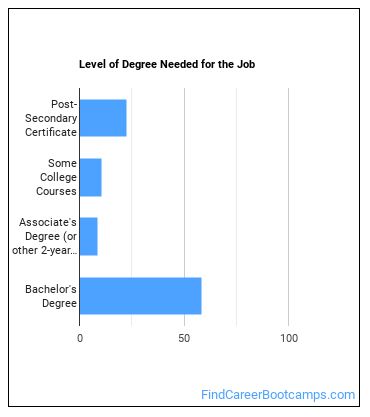
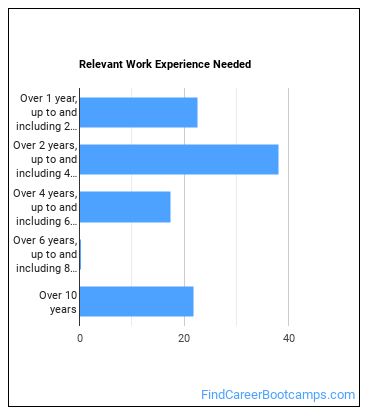
What work experience do I need to become an Electromechanical Engineering Technologist?
Who Employs Electromechanical Engineering Technologists?
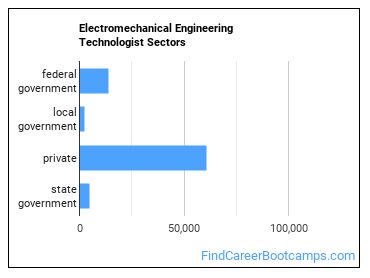
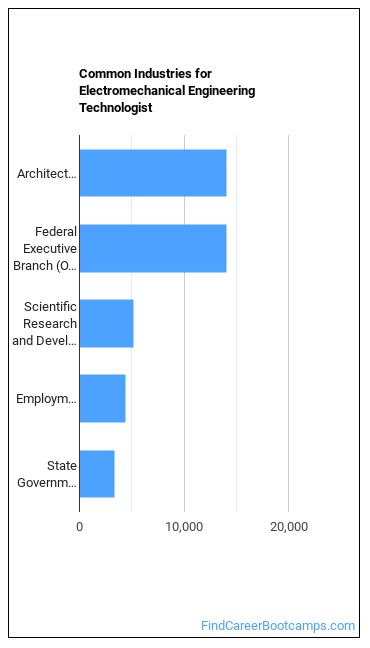
The table below shows the approximate number of Electromechanical Engineering Technologists employed by various industries.
References:
Image Credit: Airman 1st Class Ryan Conroy via Public domain
More about our data sources and methodologies.
